The G8+5 Climate Change Dialogue was launched on February 24, 2006, by the ([[GLOBE]])<ref>{{usurped|1=[https://web.archive.org/web/20070312185053/http://www.globeinternational.org/index.php GLOBE international]}}</ref> in partnership with the ”Com+” alliance of communicators for sustainable development.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.complusalliance.org/ |title=Com+ alliance |access-date=2007-02-17 |archive-date=2022-02-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220202133023/http://www.complusalliance.org/ |url-status=dead }}</ref>
The G8+5 Climate Change Dialogue was launched on February 24, 2006, by the ([[GLOBE]])<ref>{{usurped|1=[https://web.archive.org/web/20070312185053/http://www.globeinternational.org/index.php GLOBE international]}}</ref> in partnership with the ”Com+” alliance of communicators for sustainable development.<ref>{{Cite web |url=http://www.complusalliance.org/ |title=Com+ alliance |access-date=2007-02-17 |archive-date=2022-02-02 |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20220202133023/http://www.complusalliance.org/ |url-status=dead }}</ref>
==Institutionalization==
==Institutionalization==
{{Anchor|Heiligendamm Process}}
Following the [[33rd G8 summit]] [[Heiligendamm]] 2007, German chancellor [[Angela Merkel]] announced the establishment of the “[[Heiligendamm Process]]” through which the full institutionalization of the permanent dialogue between the G8 countries and the five greatest [[emerging economies]] will be implemented. This will include the establishment of a common G8 and G5 platform at the [[OECD]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Die G8 – Akteure in einer globalen Entwicklungspartnerschaft |url=http://www.bmz.de/de/service/infothek/fach/spezial/index.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080217222220/http://www.bmz.de/de/service/infothek/fach/spezial/index.html |archive-date=2008-02-17}}</ref>
Following the [[33rd G8 summit]] [[Heiligendamm]] 2007, German chancellor [[Angela Merkel]] announced the establishment of the “Heiligendamm Process” through which the full institutionalization of the permanent dialogue between the G8 countries and the five greatest [[emerging economies]] will be implemented. This will include the establishment of a common G8 and G5 platform at the [[OECD]].<ref>{{Cite web |title=Die G8 – Akteure in einer globalen Entwicklungspartnerschaft |url=http://www.bmz.de/de/service/infothek/fach/spezial/index.html |url-status=dead |archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20080217222220/http://www.bmz.de/de/service/infothek/fach/spezial/index.html |archive-date=2008-02-17}}</ref>
Most recently on August 28, 2007, former French president [[Nicolas Sarkozy]] in a foreign policy statement proposed that [[Brazil]], [[China]], [[India]], [[Mexico]] and [[South Africa]] should become members of G8: “The G8 can’t meet for two days and the G13 for just two hours…. That doesn’t seem fitting, given the power of these five emerging countries.” Nevertheless, as of 2008, a formal enlargement of the G8 is not a realistic political option, since the G8 member states have diverging positions on this issue. The [[United States]] and [[Japan]] have been against enlargement, the [[United Kingdom]] and [[France]] actively in favour, and [[Italy]], [[Germany]], [[Russia]] and [[Canada]] are reserved on the issue.{{Citation needed|date=April 2008}}.
August 28, 2007, French president [[Nicolas Sarkozy]] in a foreign policy statement proposed that [[Brazil]], [[China]], [[India]], [[Mexico]] and [[South Africa]] should become members of G8: “The G8 can’t meet for two days and the G13 for just two hours…. That doesn’t seem fitting, given the power of these five emerging countries.”
Innovation, freedom of investment, development in Africa, and technology for reducing [[greenhouse gas|{{CO2}} emission]]s were the four main issues this process visited in 2008 and 2009. A progress report was presented at the [[34th G8 summit|2008 G8 Summit]] in Japan; a final report on the results of the dialogue was put forward in [[35th G8 summit|Italy in 2009]]. [[German Chancellor]] [[Angela Merkel]] supported this process, stating, “[W]e cannot get by, or shape globalization in a humane way, without each other”.
Nevertheless, as of 2008, a formal enlargement of the G8 was not a realistic political option, since the G8 member states have diverging positions on this issue. The United States and Japan have been against enlargement, the United Kingdom and France actively in favour, and Italy, Germany, Russia and Canada are reserved on the issue.{{Citation needed|date=April 2008}}.
==Leaders in March 2014==
==Leaders in March 2014==
Organization

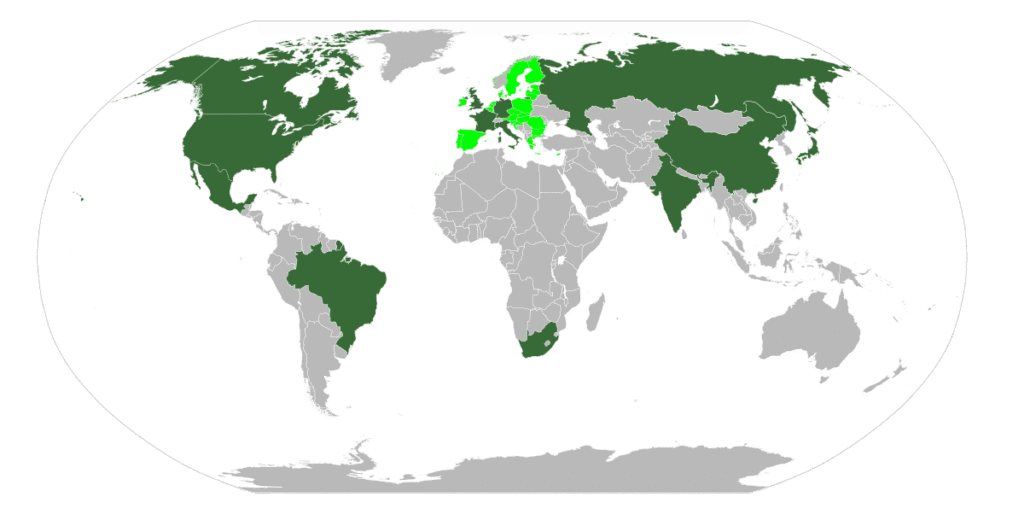
Members of the G8+5 are highlighted in dark green. Members of the European Union are highlighted in light green.
|
|
| Abbreviation | G8+5 |
|---|---|
The Group of Eight + Five (G8+5) was an international group that consisted of the leaders of the heads of government from the G8 nations (Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Russia, the United Kingdom, and the United States), plus the heads of government of the five leading emerging economies (Brazil, China, India, Mexico, and South Africa). In March 2014, Russia was removed from the Group of 8 for annexing Crimea,[1] so the G8+5 in its original form is unlikely to reconvene with Russia present.
February 2007 declaration
[edit]
On February 16, 2007, The Global Legislators Organisation (GLOBE International) held a meeting of the G8+5 Climate Change Dialogue at the GLOBE Washington Legislators Forum in Washington, D.C., where a non-binding agreement was reached to cooperate on tackling global warming. The group accepted that the existence of man-made climate change was beyond doubt, and that there should be a global system of emission caps and carbon emissions trading applying to both industrialized nations and developing countries. The group hoped this policy to be in place by 2009, to supersede the Kyoto Protocol, the first phase of which expires in 2012.[2][3]
The G8+5 group was formed in 2005 when Tony Blair, then Prime Minister of the United Kingdom, in his role as host of the 31st G8 summit at Gleneagles, Scotland, invited the leading emerging countries to join the talks. The hope was that this would form a stronger and more representative group that would inject fresh impetus into the trade talks at Doha, and the need to achieve a deeper cooperation on climate change.
Following the meeting, the countries issued a joint statement looking to build a “new paradigm for international cooperation” in the future.
The G8+5 Climate Change Dialogue was launched on February 24, 2006, by the (GLOBE)[4] in partnership with the Com+ alliance of communicators for sustainable development.[5]
Institutionalization attempt
[edit]
Following the 33rd G8 summit, Heiligendamm 2007, German chancellor Angela Merkel announced the establishment of the “Heiligendamm Process” through which the full institutionalization of the permanent dialogue between the G8 countries and the five greatest emerging economies will be implemented. This will include the establishment of a common G8 and G5 platform at the OECD.[6]
On August 28, 2007, French president Nicolas Sarkozy in a foreign policy statement proposed that Brazil, China, India, Mexico and South Africa should become members of G8: “The G8 can’t meet for two days and the G13 for just two hours…. That doesn’t seem fitting, given the power of these five emerging countries.”
Innovation, freedom of investment, development in Africa, and technology for reducing CO2 emissions were the four main issues this process visited in 2008 and 2009. A progress report was presented at the 2008 G8 Summit in Japan; a final report on the results of the dialogue was put forward in Italy in 2009. German Chancellor Angela Merkel supported this process, stating, “[W]e cannot get by, or shape globalization in a humane way, without each other”.
Nevertheless, as of 2008, a formal enlargement of the G8 was not a realistic political option, since the G8 member states have diverging positions on this issue. The United States and Japan have been against enlargement, the United Kingdom and France actively in favour, and Italy, Germany, Russia and Canada are reserved on the issue.[citation needed].
Leaders in March 2014
[edit]
The following list is a list of leaders of G8+5 in March 2014, when Russia was suspended from the G8. It is in alphabetical order by nation.



![China Xi Jinping, President[a]](https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/3/32/Xi_Jinping_2019.jpg/120px-Xi_Jinping_2019.jpg)













